Leveraging AI for Enhanced Knowledge Work
Jan 29, 2025

The Future of Knowledge Work with AI
As we look towards the year 2025, a startling prediction emerges: it will take more time to read and comprehend content than it does to create it. This highlights a growing challenge in our digital age, where the sheer volume of information continues to expand. The proliferation of AI-generated content, often seen in the form of repetitive posts on platforms like LinkedIn and SEO-driven blog posts, contributes significantly to this overwhelming noise.
In twenty twenty five, it will take you longer to read something and comprehend it than the amount of time it took to create it.
So if you think finding the signal within all that noise is only going to get worse with all that AI generated regurgitation of posts on LinkedIn and all that SEO optimized blog posts that don't actually contain anything good.
The challenge we face is not just about volume but about quality. Amidst this sea of content, finding valuable and meaningful information becomes increasingly difficult. This situation necessitates a strategic approach where we leverage AI not just for content creation but for elevating our position within the knowledge value chain.
In this section, we will explore how AI can help us sift through this noise and enhance our capacity for meaningful knowledge work.
Understanding the Knowledge Work Value Chain
The knowledge work value chain is a concept that can greatly benefit from the integration of AI technologies. To fully leverage its potential, it's essential to revisit the fundamentals of knowledge work and identify areas for improvement.
So let's come back to the fundamentals of knowledge work and find where we can get leverage.
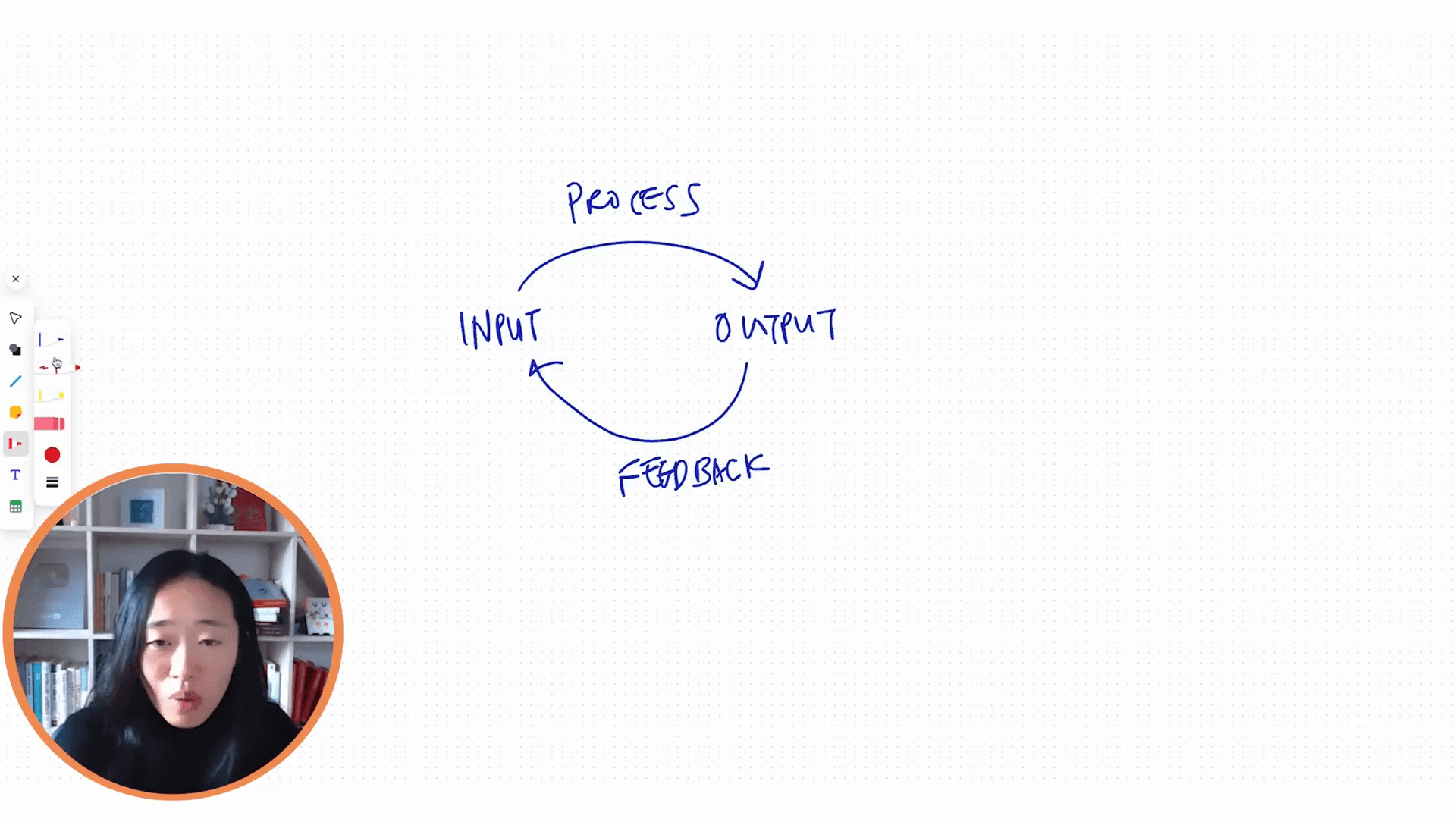
Knowledge work can be broken down into a four-step process:
Input: This is where we gather data, knowledge, and information. The quality of input is crucial as it sets the foundation for everything that follows.
Processing: Once the input is gathered, it is processed to produce an output.
Output: The result of processed information.
Feedback and Improvement: Using feedback from the output to refine and enhance the input.
This cycle creates a continuous loop, where each iteration aims to enhance the quality of knowledge work. Over time, this process leads to an upward spiral—constantly improving and refining all aspects of knowledge work.
And over time, we're going to spiral upwards.
The importance of improving input quality cannot be overstated. With AI's ability to enhance these inputs, organizations can significantly boost their efficiency and effectiveness in generating valuable outputs.
The Role of AI in Improving Inputs
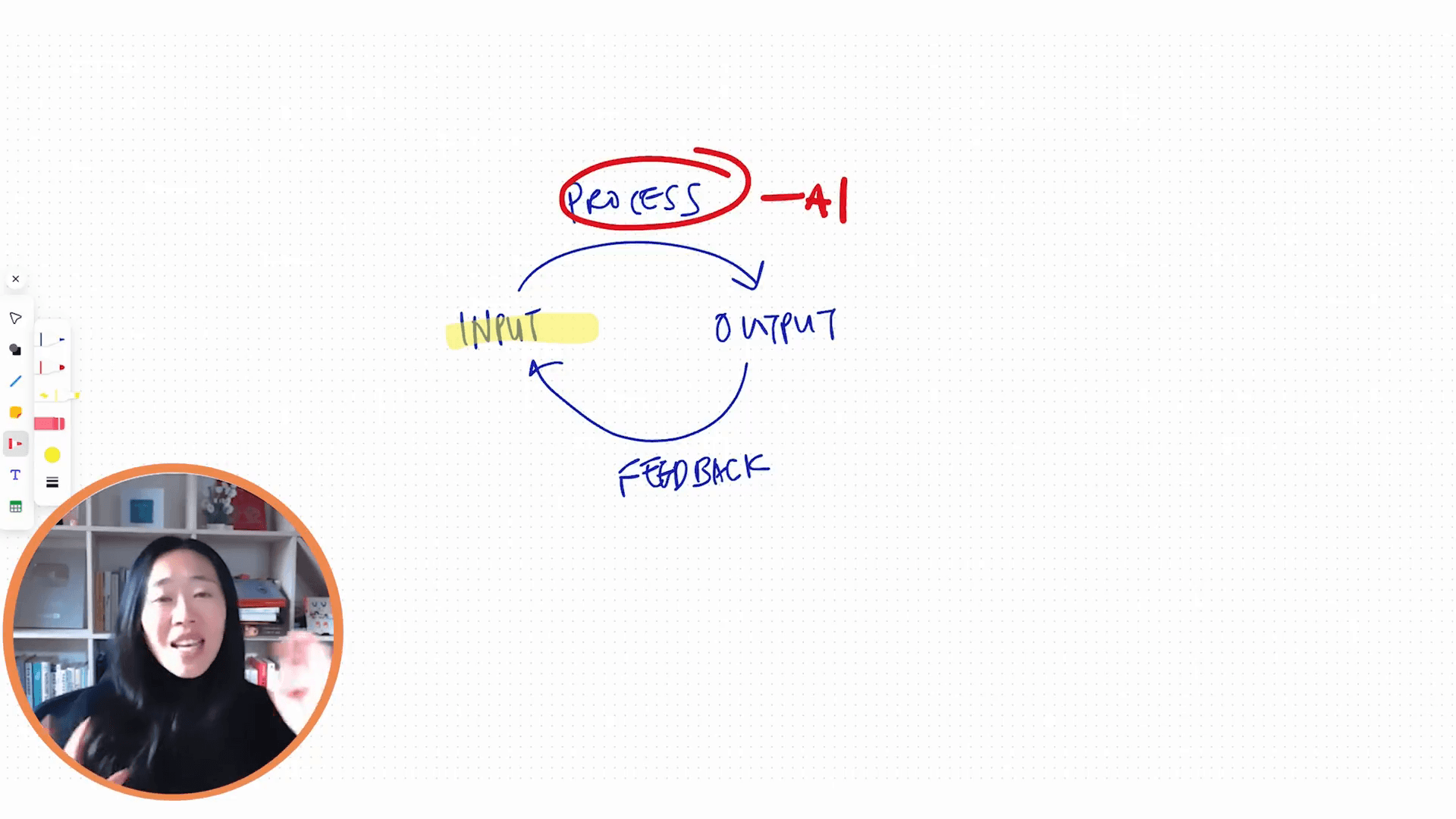
In today's rapidly advancing technological landscape, many individuals find themselves pondering the question: "How can I outsource my thinking process to AI?" With the rise of tools such as Claude and ChatGPT, the temptation to delegate tasks to artificial intelligence is stronger than ever. However, the results aren't always as spectacular as one might hope.
"Most people spend the majority of their time thinking about how can I outsource my thinking process to AI?"
The crux of the issue lies in the inputs that large language models (LLMs) receive. Often, these inputs are quite average, reflecting a broad and generalized spectrum of information available on the Internet. While there are nuggets of valuable data amidst this vast sea, a significant portion remains mediocre.
This average quality leads to a dilution of potential output quality, often referred to as the "garbage in, garbage out" problem. When LLMs are fed with subpar data, their outputs naturally mirror that quality.
Instead of fixating on refining our processes, there is a growing recognition that focusing on enhancing our inputs can yield significantly better results. By elevating the quality of information fed into these models, even if our processing methods remain static, we can achieve superior outputs.
The feedback loop involving inputs and outputs is crucial here. With improved inputs, we break free from mediocrity and harness AI's true potential for delivering exceptional results.
Incorporating Academic Research into Inputs
In the evolving landscape of knowledge work, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into our processes is proving to be a game changer. A significant part of this transformation lies in enhancing our inputs. One of the pivotal strategies we are going to adopt is to incorporate academic papers and research into our array of inputs.
The eighty twenty we're going to do here is to add academic papers and research into our input.
Initially, this might seem tedious—perhaps even boring. You might wonder why we are venturing into what appears to be a domain reserved for academia when we are focused on practical work. The truth is, practical outcomes are exactly what we need, and academic research can be a treasure trove of insights if leveraged correctly.
Consider the sources like Harvard Business Review, McKinsey Quarterly, or MIT Sloan Review. Do you read these? These publications are masters at taking what may seem like complex and dry academic papers and transforming them into content that is both relevant and actionable for working professionals.
Do you read Harvard Business Review or McKinsey Quarterly or the MIT Sloan Review?
The key here is not just to be passive readers but to harness the potential within these resources actively. These publications expertly distill dense academic insights into actionable strategies that can drive real-world results. Our goal is not just to consume this information but to become a source of valuable insights ourselves—much like these revered publications.
The task at hand involves recognizing the value embedded within academic research and effectively translating that knowledge into practical applications that can enhance our work processes and outcomes.
Tools for Accessing and Utilizing Academic Papers
In today's fast-paced world, the ability to effectively access and utilize academic papers has become a crucial skill for many professionals. The traditional approach of slowly reading through volumes of journals, such as the Harvard Business Review (HBR), is no longer efficient. As one might say, "We read so slowly, but if you just feed the entire archive to ChatGPT, immediately, it will know so much more than you."
This is where tools like Elicit and Notebook LM come into play. These tools are designed to help you become the HBR for your team or organization. By accessing trusted resources that are complex and nuanced, you can translate extensive theoretical knowledge into actionable insights. The goal is to create frameworks that busy professionals can easily understand and apply.
"Let me show you the three tools that I use to make sure I become, you know, HBR for my team."
One of the biggest challenges managers face is dealing with team underperformance. To address this, Elicit can be an invaluable tool. It allows you to process large amounts of information quickly and extract relevant insights without needing to spend years on research.
By leveraging these tools, we are moving up the value chain—engaging with content that was traditionally reserved for academics or authors who had both time and resources on their side. Now, with these innovative solutions at our fingertips, anyone can delve into lengthy papers and extract valuable insights efficiently.
Creating Actionable Insights from Academic Research
In the quest to transform into the Harvard Business Review (HBR) for your team or organization, leveraging academic research can be a game-changer. One of the most pressing issues managers face is team underperformance. You might have bright individuals on your team, yet they seem disengaged or constantly dissatisfied. How can you effectively boost team performance?
Often, when seeking solutions to such challenges, the default approach might involve consulting tools like ChatGPT or performing a general Google search. However, these methods typically yield generic advice such as "focus on goals" or "encourage open communication"—suggestions that are broad and lack depth.
Instead, I recommend utilizing a tool called Elicit. This tool helps you find academic papers related to your query, providing summaries of the top papers and a list of related scholarly articles. This service is free; you just need to sign up.
You get the summary of the top four papers.
Once you have these results, it's crucial to ensure that what you are reading is credible and well-cited. I prefer sorting results by "most cited" to prioritize impactful research. For instance, if you're interested in exploring how team design impacts performance, Elicit can guide you towards relevant studies.
After identifying a promising paper in Elicit, you can click into Semantic Scholar for more details. Sometimes access might be restricted if you don't have a university subscription, but don't worry—there's often a workaround. Copy and paste the title into Google to find a freely accessible PDF version.
By utilizing these steps and tools effectively, managers can derive actionable insights from academic research that go beyond generic advice and truly enhance team performance.
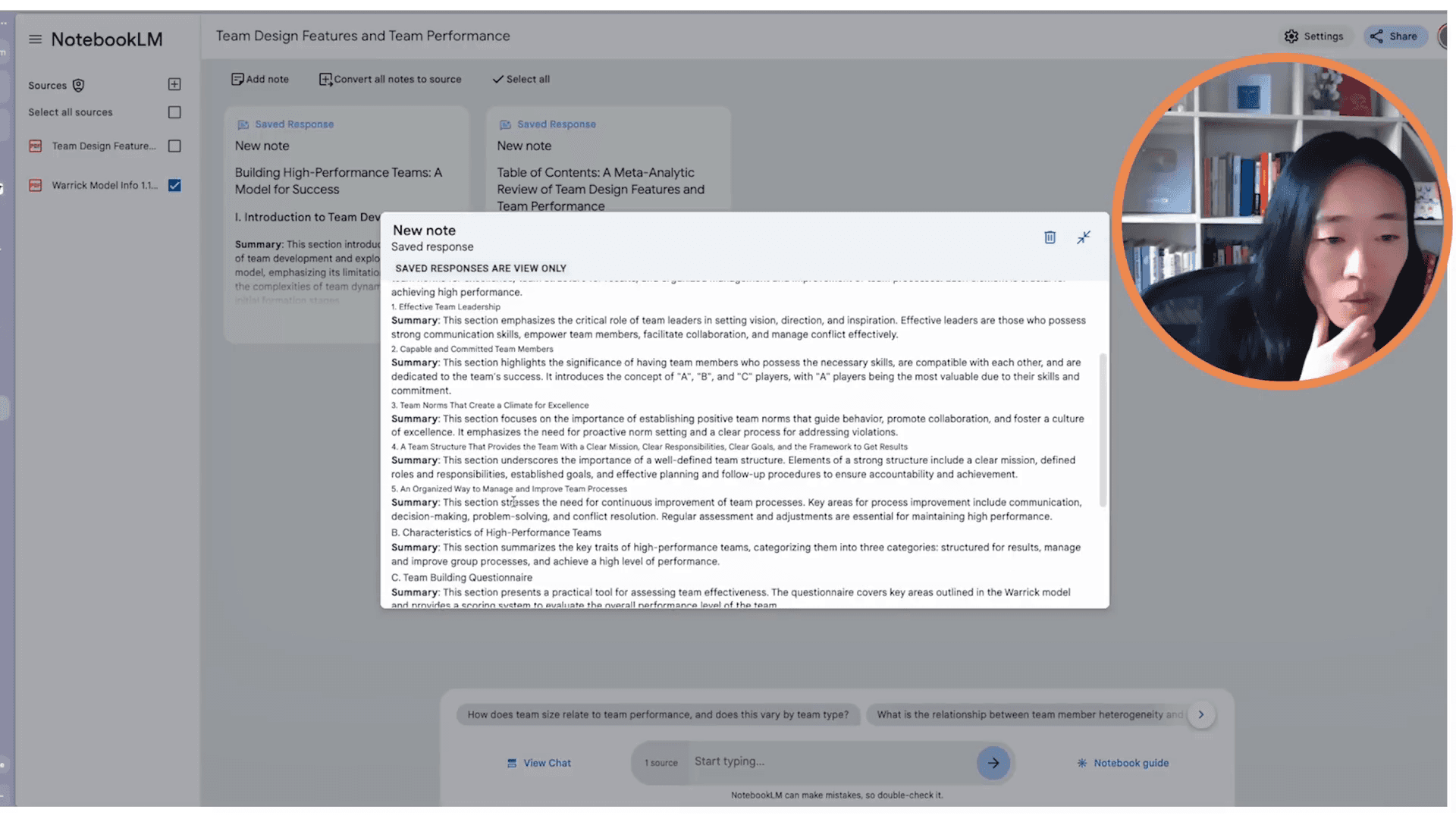
Utilizing Notebook LM for Detailed Analysis
Using Notebook LM by Google offers a unique approach to analyzing academic papers. Unlike other AI tools like ChatGPT or Claude, Notebook LM focuses solely on the sources you upload, significantly reducing the chances of hallucinations. By signing in with a Google account, users can create a notebook to house their sources, such as a PDF file.
"We are going to just upload it here."
Once the PDF is uploaded, Notebook LM automatically generates a table of contents. This feature is particularly useful for gaining an overview of the paper's structure without having to read it in its entirety immediately. For instance, topics such as group classification theory, team size, task design, and leadership are identified as key sections.
After establishing a general understanding from the table of contents, users can explore suggested questions generated by the AI. This feature helps in grasping the core concepts without delving into extensive text.
"I usually like to use one of the questions just to give me the basic gist."
An example question might be: "How do team design features impact overall team performance?" This query helps isolate essential components like team composition, task design, and leadership—elements that are also highlighted in the table of contents.
One of Notebook LM's standout features is its ability to direct users to specific parts of the source material referenced by these questions. This allows for efficient navigation and deeper dives into sections of interest.

Combining Insights for Comprehensive Strategies
In the quest to build high-performing teams, it's crucial to integrate insights from various academic papers and sources. The process begins with identifying the most pertinent information from extensive research. For example, when dealing with thousands of words of content, it's essential to discern which parts are most relevant and find the corresponding citations for a deeper understanding.
Sometimes, constraints like team composition cannot be altered—you can't just hire or fire team members on a whim. However, you can focus on adapting task design and leadership strategies. This is where AI tools like Elicit and Notebook LM come into play, offering a workflow that allows users to pinpoint key areas from academic papers that can be applied directly to team dynamics.
Initially, this process might involve reviewing a single paper. By returning to tools like Elicit, you can search for additional relevant papers on topics such as team leadership or developing high-performance teams. Even when access issues arise, such as encountering a bad request while trying to download a PDF from sources like Wiley, persistence often leads to success in obtaining the needed documents through alternative means.
Once multiple sources have been uploaded into Notebook LM, you can interact with them simultaneously. For instance, by deselecting older sources and focusing solely on new ones, you gain clarity on the fresh insights they offer. For example, one paper might outline five essentials for building high-performance teams: leadership, capable and committed members, clear norms and team structure with defined missions and responsibilities.
This method is far more efficient than relying on diluted information from secondary sources found through general searches. By directly engaging with original research documents and utilizing AI tools for analysis, leaders can craft comprehensive strategies that leverage academic insights effectively.

There are five essentials to building high performance teams.
Refining Strategies with AI Tools
In the evolving landscape of team management, AI tools are becoming invaluable for refining leadership strategies. As leaders seek to boost team performance, the integration of AI tools like Claude and Notebook LM offers promising avenues for simplifying and enhancing strategic planning.
The process begins with identifying key components that can drive performance improvements. By analyzing sources for actionable insights, leaders can focus on essential areas such as promoting task meaningfulness and empowering teams with autonomy. As highlighted in the transcript, the effective leadership component involves guiding, motivating, and supporting team members to achieve their best.
"Help me create a detailed plan to improve team performance."
Initially, a high-level plan may seem vague despite being grounded in academic research. This is where AI tools step in to refine these strategies into detailed actionable steps. For instance, Claude can be used to transform these inputs into a comprehensive twelve-month, three-phase plan that is not only thorough but also impressive enough to present to management.
However, complexity can be overwhelming. To address this, leaders can leverage the Pareto Principle—commonly known as the 80/20 rule—to identify which changes will yield the most significant improvements with minimal effort. By asking what changes depend primarily on leadership rather than team members, leaders can focus on making impactful adjustments that align with research-backed strategies.
The collaboration between AI tools and leadership not only streamlines planning but also ensures that strategies are both innovative and grounded in credible research. This synergy is essential for driving sustainable improvements in team performance.
Conclusion: Embracing AI for Knowledge Work
As we conclude our exploration of AI's transformative role in knowledge work, there's a palpable sense of excitement and optimism about the journey ahead. The integration of AI into knowledge workflows is not just about efficiency; it's about enhancing our capability to think critically and creatively.
Claude's insights into task design optimization, authority distribution, and contextual support exemplify the potential of AI in refining processes that traditionally took months into streamlined strategies that only require a fraction of the time. The shift from a twelve-month to a three-month timeline for achieving expected results underscores the power of AI-driven insights.
"I am excited and optimistic about the changes coming to knowledge work."
This optimism is not unfounded. By leveraging AI, we open doors to new dimensions of creativity and problem-solving. The future of knowledge work is promising, offering us tools to not only enhance our productivity but also to foster innovation and deeper understanding.
In embracing these changes, we are encouraged to think critically about how these tools can be applied most effectively in our own contexts.
Let us continue this dialogue and explore how you feel about these advancements in AI for knowledge work.

Mental reframe
Actionable frameworks content every week.
Subscribe (it’s free):